PhysLab.net – Double Pendulum
This is a simulation of a double pendulum. For large motions it is a chaotic system, but for small motions it is a simple linear system.
You can change parameters in the simulation such as mass, gravity, and length of rods (enable the "show controls" checkbox). You can drag the pendulum with your mouse to change the starting position. If you don't see the simulation try instructions for enabling Java. Scroll down to see the math!
Instructions: click near circles and drag with your mouse
To purchase a professionally
engineered chaotic pendulum,
click
here.

For small angles, a pendulum behaves like a
linear system (see
Simple Pendulum). When the angles are small in the Double Pendulum, the system behaves like the linear
Double Spring. In the graph, you can see similar
Lissajous curves being generated. This is because the motion is determined by simple sine and cosine functions.
For large angles, the pendulum is non-linear and the phase graph becomes much more complex. You can see this by dragging one of the masses to a larger angle and letting go.
We regard the pendulum rods as being massless and rigid. We regard the pendulum masses as being point masses. The derivation of the equations of motion is shown below, using the direct Newtonian method.
Kinematics of the Double Pendulum
Kinematics means the relations of the parts of the device, without regard to forces. In kinematics we are only trying to find expressions for the position, velocity, & acceleration in terms of the variables that specify the state of the device.
- x = horizontal position of pendulum mass
- y = vertical position of pendulum mass
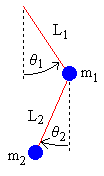
- θ = angle of pendulum (0 = vertical downwards, counter-clockwise is positive)
- L = length of rod (constant)
We place the origin at the pivot point of the upper pendulum. We regard
y as increasing upwards. We indicate the upper pendulum by subscript 1, and the lower by subscript 2. Begin by using simple trigonometry to write expressions for the positions
x1, y1, x2, y2 in terms of the angles
θ1, θ2.
x1 = L1 sin θ1
y1 = −L1 cos θ1
x2 = x1 + L2 sin θ2
y2 = y1 − L2 cos θ2
The velocity is the derivative with respect to time of the position.
x1' = θ1' L1 cos θ1
y1' = θ1' L1 sin θ1
x2' = x1' + θ2' L2 cos θ2
y2' = y1' + θ2' L2 sin θ2
The acceleration is the second derivative.
| |
x1'' = −θ1'2 L1 sin θ1 + θ1'' L1 cos θ1
| (1) |
| |
y1'' = θ1'2 L1 cos θ1 + θ1'' L1 sin θ1
| (2) |
| |
x2'' = x1'' − θ2'2 L2 sin θ2 + θ2'' L2 cos θ2
| (3) |
| |
y2'' = y1'' + θ2'2 L2 cos θ2 + θ2'' L2 sin θ2
| (4) |
Forces in the Double Pendulum
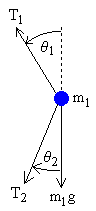
upper mass
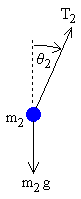
lower mass
We treat the two pendulum masses as point particles. Begin by drawing the free body diagram for the upper mass and writing an expression for the net force acting on it. Define these variables:
- T = tension in the rod
- m = mass of pendulum
- g = gravitational constant
The forces on the upper pendulum mass are the tension in the upper rod
T1, the tension in the lower rod
T2, and gravity
−m1 g. We write separate equations for the horizontal and vertical forces, since they can be treated independently. The net force on the mass is the sum of these. Here we show the net force and use Newton's law
F = m a.
| |
m1 x1'' = −T1 sin θ1 + T2 sin θ2
| (5) |
| |
m1 y1'' = T1 cos θ1 − T2 cos θ2 −
m1 g
| (6) |
For the lower pendulum, the forces are the tension in the lower rod
T2, and gravity
−m2 g.
| |
m2 y2'' = T2 cos θ2 − m2 g
| (8) |
In relating these equations to the diagrams, keep in mind that in the example diagram
θ1 is positive and
θ2 is negative, because of the convention that a counter-clockwise angle is positive.
Direct Method for Finding Equations of Motion
Now we do some algebraic manipulations with the goal of finding expressions for
θ1'', θ2'' in terms of
θ1, θ1', θ2, θ2'. Begin by solving equations (7), (8) for
T2 sin θ2 and
T2 cos θ2 and then substituting into equations (5) and (6).
| |
m1 x1'' = −T1 sin θ1 − m2 x2''
| (9) |
| |
m1 y1'' = T1 cos θ1 − m2 y2'' − m2 g −
m1 g
| (10) |
Multiply equation (9) by
cos θ1 and equation (10) by
sin θ1 and rearrange to get
| |
T1 sin θ1 cos θ1 = −cos θ1 (m1 x1'' +
m2 x2'')
| (11) |
| |
T1 sin θ1 cos θ1 = sin θ1 (m1 y1'' + m2 y2'' +
m2 g +
m1 g)
| (12) |
This leads to the equation
| |
sin θ1 (m1 y1'' + m2 y2'' + m2 g +
m1 g) =
−cos θ1 (m1 x1'' + m2 x2'')
| (13) |
Next, multiply equation (7) by
cos θ2 and equation (8) by
sin θ2 and rearrange to get
| |
T2 sin θ2 cos θ2 = −cos θ2 (m2 x2'')
| (14) |
| |
T2 sin θ2 cos θ2 = sin θ2 (m2 y2'' + m2 g)
| (15) |
which leads to
| |
sin θ2 (m2 y2'' + m2 g) = −cos θ2 (m2 x2'')
| (16) |
Next we need to use a program such as
Mathematica to solve equations (13) and (16) for
θ1'', θ2'' in terms of
θ1, θ1', θ2, θ2'. Note that we also include the definitions given by equations (1-4), so that we have 2 equations (13, 16) and 2 unknowns (
θ1'', θ2''). The result is somewhat complicated, but is easy enough to program into the computer.
|
θ1'' =
|
−g (2 m1 + m2) sin θ1 − m2 g sin(θ1 − 2 θ2) − 2 sin(θ1 − θ2) m2 (θ2'2 L2 + θ1'2 L1 cos(θ1 − θ2))
|
|
L1 (2 m1 + m2 − m2 cos(2 θ1 − 2 θ2))
|
|
θ2'' =
|
2 sin(θ1 − θ2) (θ1'2 L1 (m1 + m2) + g(m1 + m2) cos θ1 + θ2'2 L2 m2 cos(θ1 − θ2))
|
|
L2 (2 m1 + m2 − m2 cos(2 θ1 − 2 θ2))
|
These are the equations of motion for the double pendulum.
Numerical Solution
The above equations are now close to the form needed for the
Runge-Kutta method. The final step is convert these two 2nd order equations into four 1st order equations. Define the first derivatives as separate variables:
- ω1 = angular velocity of top rod
- ω2 = angular velocity of bottom rod
Then we can write the four 1st order equations:
θ1' = ω1
θ2' = ω2
|
ω1' =
|
−g (2 m1 + m2) sin θ1 − m2 g sin(θ1 − 2 θ2) − 2 sin(θ1 − θ2) m2 (ω22 L2 + ω12 L1 cos(θ1 − θ2))
|
|
L1 (2 m1 + m2 − m2 cos(2 θ1 − 2 θ2))
|
|
ω2' =
|
2 sin(θ1−θ2) (ω12 L1 (m1 + m2) + g(m1 + m2) cos θ1 + ω22 L2 m2 cos(θ1 − θ2))
|
|
L2 (2 m1 + m2 − m2 cos(2 θ1 − 2 θ2))
|
This is now exactly the form needed to plug in to the Runge-Kutta method for numerical solution of the system.